Types of Evaluation Small Group One-on-one Expert Review
- Chapter 10, Designing and Conducting Formative Evaluations, from Dick and Carey.
- Tessmer, M. (1997). Planning and conducting determinative evaluations. London: Kogan Page.
Now that you lot've developed your multimedia program, you may think that yous're finally finished. Hooray! Washed! On to the adjacent project! Unfortunately, many projects end this style, and never realize their true potential considering they are not run through an evaluation process. Allow's take i concluding expect at the Dick and Carey model of instructional design. Notice where nosotros are and you tin can run into that developing your instructional materials is not the last step in their ID model. In that location'south nonetheless a couple of boxes dealing with different types of evaluation.
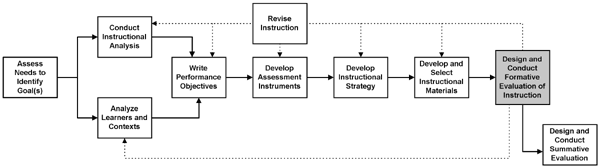
Notice the dotted lines coming out and pointing dorsum to earlier steps, along with the box that says "Revise Instruction". These things indicate that the ID procedure in non completely linear. Each step tin can be revisited equally feedback is received from the evaluation procedures. Indeed, that'south the point of conducting a formative evaluation.
Formative evaluation involves the collection of information and information during the evolution process that can be used to better the effectiveness of the didactics. Determinative means that the instructional materials are in their formative, or early stages, and evaluation refers to the process of gathering data to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the didactics. "Thus, formative evaluation is a judgment of the strengths and weaknesses of instruction in its developing stages, for the purposes of revising the education to improve its effectiveness and entreatment" (Tessmer, 1997, p. 11). Any grade of instruction that can still be revised is a potential candidate for formative evaluation. This includes paper-based educational activity, computer-based instruction, alive lectures, and workshops.
Evaluation is ane of the most important steps in the pattern procedure, and yet it's unremarkably the step that gets left out. Many instructional projects are never evaluated with experts or actual learners prior to their implementation. The trouble with that is that the designers and developers are frequently "too close" to the project and lose their power to evaluate the effectiveness of what they are working on (forest - trees - yadda yadda). For that reason, information technology'due south imperative that y'all bring in people from outside of the process to assistance you make up one's mind if you are truly hitting the mark, or if some minor (or major) adjustments are in order to bring the instruction up to its full potential.
Formative evaluation procedures can be used throughout the pattern and evolution process. Yous probably have already formatively evaluated your materials in the procedure of developing them. Yous might lay out components on the screen, try them out, and then motility them effectually if they are not exactly right. Or, you might write some instructional text, endeavour it out to come across if you call up information technology addresses the objective, and so rewrite it to make a better friction match. At this betoken, though, it's fourth dimension to seek exterior help. Fifty-fifty trying out instructional materials with a single learner tin point out obvious flaws and lead to revisions that can accept a major impact on the effectiveness of the didactics. Remember of it more as a trouble-finding stage of the instructional design procedure, not as a carve up process birthday.
The other type of evaluation is Summative Evaluation. Summative evaluation is conducted when the instructional materials are in their final form, and is used to verify the effectiveness of instructional materials with the target learners. The main purpose is unremarkably to make decisions about the conquering or continued utilise of certain instructional materials, or to determine if the instruction is better than some other class of teaching. We will non deal with summative evaluation in this course, simply experience free to read Chapter 12 in the Dick and Carey book if you would like more information nearly the topic.
Martin Tessmer, in his book Planning and Conducting Formative Evaluations, details the stages of the formative evaluation process. According to Tessmer, there are four stages of determinative evaluation:
- Skillful Review
- I-to-1
- Small Group
- Field Test
Each stage is carried out in order to accomplish different things, and to progressively improve the instruction. During the evaluation information is collected from experts and members of the target population. While you may collect performance data during some stages of the procedure, keep in mind that formative evaluation is non concerned with testing the learners, but with testing the instruction itself.
The tables in the following sections provide a rundown of each stage of formative evaluation.
In this stage, experts review the instruction with or without the evaluator present. These people can be content experts, technical experts, designers, or instructors.
| Expert Review | |
| What is the purpose of this evaluation blazon? | The expert review looks at the intrinsic aspects of the instruction. these include things like the content accuracy or technical quality. The instruction is mostly not evaluated in terms of learner performance or motivation. |
| When is this type of evaluation usually conducted? | Proficient review is ordinarily the first footstep in the evaluation procedure and should be conducted as early in the ID process as possible. |
| Who usually conducts this type of evaluation? | Instructional designer(s) |
| Who should participate in the evaluation? | One or more than of the following experts "walks" through the material with or without the evaluator present:
|
| What planning strategies should the evaluator employ prior to conducting the evaluation? | Decide what information is needed from the review and prepare questions in advance. The following types of information are usually collected at this stage:
|
| What procedure should be followed during the evaluation? | Set up the expert for the review.
|
| What data should exist collected? | Based on general comments every bit recorded by the expert as well as designer, the post-obit types of data are usually collected during an skilful review:
|
| How should the data be analyzed? | Organize all information to help make revision decisions:
|
| What is the terminal production? | "To exercise" list for all revisions to exist made. |
| What are some of the special problems and concerns facing the evaluator(s)? |
|
This is probably the most utilized form of determinative evaluation. In this stage, one learner at a time reviews the instructional materials with the evaluator present. The evaluator observes how the learner uses the instruction, notes the learner's comments, and poses questions to the learner during and afterward the instruction.
| I-to-I Evaluation | |
| What is the purpose of this evaluation type? | The purpose of the 1-to-one evaluation is to identify the following:
|
| When is this type of evaluation usually conducted? | One-to-one evaluations are usually conducted after the expert review evaluation but before any other blazon of formative evaluation. |
| Who usually conducts this type of evaluation? | Instructional designer |
| Who should participate in the evaluation? | The evaluator "walks" through the textile with a trial learner. If possible, this type of evaluation should be repeated with other trial learners representing different skill levels, gender, ethnicity, motivation etc. within the target population. |
| What planning strategies should the evaluator utilise prior to conducting the evaluation? | The most important planning strategy is simply determining the data that needs to be collected. The information will be either intrinsic data about the instructional cloth, or data nearly the effects of the instruction. The general criteria for making this determination centers effectually how "rough" the instruction is at the point of the evaluation. The rougher information technology is, the more probable intrinsic information will exist the most useful in informing time to come revisions. Some specific criteria in judging the "roughness" of an instructional unit:
|
| What procedure should be followed during the evaluation? |
|
| What data should be collected? |
|
| How should the data exist analyzed? | All information can be evaluated at a glance, with a list of potential revisions documented. |
| What is the terminal production? | "To do" list of revisions. |
| What are some of the special problems and concerns facing the evaluator(s)? | Distant subjects - Some subjects may not exist able to make the 1-to-ane session because of logistical reasons. It is suggested that these learners withal be reached through other ways. For instance, written one-to-i questions can be inserted into the learning materials at logical breaking points in the instruction. The silent learner - Some subjects will exist reluctant to respond, often because they do non feel comfy criticizing the piece of work in the presence of its creators. This tin be addressed by warming them upward through initial conversations or by asking them some easy questions upwards front end or questions that put them in a position of say-so. Another method is to deliberately insert some errors early on in the teaching in an attempt to elicit their responses. |
In this stage, the evaluator tries out the teaching with a small group of learners and records their comments. Small-scale group evaluations typically use students as the principal subjects, and focus on performance data to confirm previous revisions and generate new ones.
| Modest Grouping Evaluation | |
| What is the purpose of this evaluation blazon? | The small group evaluation provides a "existent world" evaluation setting of learner performance. It confirms successful aspects of educational activity and offers suggestions for improvements to the implementation of the instruction and ease of administration. |
| When is this type of evaluation commonly conducted? | Minor group evaluation occurs prior to the field trial but may, unfortunately, take the place of the field trial depending upon funding and time constraints. |
| Who usually conducts this type of evaluation? | Instructional designer(s) |
| Who should participate in the evaluation? | The instructional material is administered to a group of 5-xx participants representing the target population. If possible, a representative teacher or facilitator from the target population will work closely with a member of the design squad to administer the material. |
| What planning strategies should the evaluator employ prior to conducting the evaluation? | Planning strategies are addressed in the process section beneath. The simply boosted planning might include determining if the selected learners possess the necessary prerequisite skills needed (might be apparent from pretest operation). |
| What procedure should be followed during the evaluation? |
|
| What data should be collected? | During this type of evaluation, the post-obit types of information are usually collected:
|
| How should the data be analyzed? |
|
| What is the final product? | A brief written report which includes a congruency analysis table (how many learners mastered each objective as indicated by exercise/posttest performance), implementation summaries, and attitude summaries. From this report, a "to practise" listing of revisions is generated. |
| What are some of the special issues and concerns facing the evaluator(s)? |
|
In a field exam, the instruction is evaluated in the same learning environments in which information technology will be used when finished. At this stage the instructional materials should be in their nearly polished land, although they should nonetheless be amenable to revisions.
| Field Exam | |
| What is the purpose of this evaluation type? | A field trial represents the offset time the material is used in a existent setting. All material is evaluated, paying special attending to changes made based on the minor group evaluation. Implementation procedures are also closely examined during the field trial to determine the effectiveness and feasibility of program implementation in a real class setting. The data nerveless during the field trial phase are similar, if not identical, to the data collected during a summative evaluation (primarily functioning and attitudes). In general, the field exam answers the following questions: Note that these are really even so question, just stated differently. |
| When is this type of evaluation usually conducted? | After all other formative evaluations are completed. |
| Who usually conducts this type of evaluation? | Instructional designer(south) and instructors |
| Who should participate in the evaluation? | Actual members of the target population (individuals and/or classes), including both learners and instructors. If the material is designed for an unabridged form, endeavor to use a class that is similar in size and variability as the target population (25-30 is often the norm). |
| What planning strategies should the evaluator utilize prior to conducting the evaluation? | Same every bit small group |
| What procedure should be followed during the evaluation? | Same as small group |
| What data should exist nerveless? | Same as small group |
| How should the information be analyzed? | Same as pocket-size grouping |
| What is the final product? | The concluding product is an evaluation report, emphasizing prescriptions for revision. |
| What are some of the special problems and concerns facing the evaluator(s)? | Too many sites to observe - Yous may non be able to go to all of the sites during the course of the evaluation. This volition phone call for the use of a "designated observer," which may cause the data collected to exist structurally unlike. As well much instruction to evaluate - Due to budget restrictions, you may need to cull 30-fifty% of the teaching to actually introduce into the field setting. |
At that place is much more to conducting a formative evaluation than nosotros will comprehend in this form. If you would like more information, nosotros suggest yous read Chapter x in Dick and Carey, or seek out the Tessmer book.
For this lesson, we will be using a mix between expert review and ane-to-one evaluation procedures. You will exist conducting evaluations of several other students' multimedia programs. At the aforementioned time, at that place volition be other students evaluating your plan. This means that the people who volition be evaluating your program are not from the target group of learners who yous designed the plan for, plus you lot volition non be interacting with these people face up-to-face. Even so, this evaluation method will ensure that you will receive as much objective feedback every bit possible, while at the same time allowing you to provide important feedback for others. In addition, y'all will gain experience with the formative evaluation process.
We have created an online formative evaluation interface to help manage the process of submitting and evaluating the projects. Information technology works in a similar style to the student interface you have been using to submit assignments. As students submit projects to be evaluated, everyone will automatically be assigned to different groups of non more than four students. Your assigned students volition show up in the evaluation interface. You volition evaluate the submitted multimedia project for the other students in your grouping, and they in turn will evaluate your project. When anybody is finished y'all will have several separate evaluations from which to assemble feedback that tin can be used to strengthen your program. You will non be required to actually make the changes for this grade, just you lot may want to in the hereafter. Here's the link to the interface:
Link to Evaluation Interface
Equally with the student submission interface, log in using your ITMA username and its countersign. One time you are logged in, select the appropriate module. On the next screen you will and so be presented with the evaluation options. Get-go, select the appropriate assignment number from the drop-downward box. In the other drib-downwardly box you take 3 options:
- You tin submit your project to be evaluated. This volition officially submit your projection and permit your evaluators access to it. When you submit your project, enter the URL for your project spider web page (mmfinal.htm).
- You can review the evaluations of your project. When your evaluators finish reviewing your program their scores and comments can be accessed here.
- You tin evaluate other student projects. When you select that option you will be taken to a screen list the 3 students whose projects yous must evaluate. Selecting one volition bring upward the evaluation form. The peer's project page will open in a new browser window. Be sure your browser allows pop-ups. Peers in your group volition not appear until they submit their projects.
The criteria yous use to evaluate other students' programs will be the same as the criteria listed in the last lesson (Development). These criteria will announced on the form that you apply to evaluate the programs:
- Relevance of instructional content - Is the instructional content relevant for the instructional goals and context?
- Relevance of multimedia content - Is the multimedia content relevant for the instructional goals and context?
- Appropriateness of instructional content - Is the instructional content appropriate for the audition and the discipline matter?
- Appropriateness of multimedia content - Is the multimedia content appropriate for the audience and subject thing?
- Sufficiency of instructional content - Is the instructional content sufficient to pb to the achievement of the goal?
- Sufficiency of multimedia content - Is the multimedia content sufficient to support the education?
- Instructional events - Does the program accost all of Gagne's events of instruction, except for assessment? This includes gaining attending, informing learners of the objectives, stimulating recall of prior learning, presenting the materials, providing learning guidance, providing practice and feedback, and encouraging transfer.
- Technical aspects - Do the technical aspects of the program office properly?
You lot will exist asked to rate each benchmark on a calibration from ane to five, depending on how well the program addresses that point. Cheque 1 box adjacent to each of the criterion co-ordinate to how well you feel the program meets that criterion, with one being a low score (does not meet the criterion) and five beingness a high score (meets or exceeds the criterion). In addition, there is a space for you to blazon comments next to each of the criterion. To add together comments click your mouse in the appropriate annotate box and starting time typing. These comments are very important, as they will provide of import feedback for the developer of the program. Don't worry if your comments exceed one line - information technology will just wrap to the adjacent line, which is fine. At the bottom there is infinite for you to add a summary comment.
To help guide y'all in answering these questions, we have created an evaluation chart with some relevant questions for each criterion.
Link to Evaluation Chart
Remember, the goal of formative evaluation is to better the effectiveness of your instructional materials. It consists of identifying the problems and weaknesses of the teaching and making revisions based on the data collected. With that in mind, you should not "shred" somebody's program if it is lacking in some areas. At the same time, you should be honest and constructive in your criticism. Your feedback volition exist essential to other students as they depict upward a plan for revisions. If you requite a low score in a particular area make certain to use the "Comments" field to elaborate as to why you lot did and so. Just giving a low score volition not provide a educatee with constructive enough feedback to make the required changes; your accompanying comments are essential. We conceptualize this process volition adhere to the highest standards of professional communication practices, equally we are a community of learners in which respect is an integral component. In other words, be off-white, be honest, and be respectful in your review process.
Using the feedback you receive from others, you volition now prepare a report summarizing the observations made by the evaluators and the outlining the revisions y'all would make to your plan based on that feedback. You will not actually have to make the revisions in this course. Y'all are merely drawing upwards a plan that summarizes what you learned from the evaluation procedure and what you would do to effect changes to your program.
In the start office of the report, summarize what came out of the evaluations. What did the three evaluators say most your program? What is your response to their comments? Discuss the things that are fine the fashion they are as well as the things that will need revising. This summary should cover the same areas that were covered in the evaluations: relevance, appropriateness, sufficiency, instructional events, and functionality.
In the second part of the study, for the things that need revising, describe how you would become about making those revisions. What would you lot do to solve the deficiencies? If you have content deficiencies, draw how you volition fill in these sections (due east.g. with what content?) If you have stylistic deficiencies, draw how you lot will make the necessary changes to brand things more attractive or functional.
Your evaluation study should be created in Microsoft Word. At the top of the paper type Multimedia Determinative Evaluation. Below that include your name, email address, and the engagement. When y'all save the file name it "mmevaluation". Side by side, create a link to this document from the projection web folio you created in the last lesson (mmfinal). If you used the template we provided, add a row to the bottom of the table and brand this the fifth link.
When y'all are finished, upload the Word document and the revised web folio to your Filebox. When you lot have finished uploading your files, keep to the online student interface to officially submit your activities for grading. Once again, submit the URL to your web page, non to the evaluation report. When you lot are done with that you lot are done with the grade!
Please Annotation: Information technology is very important that you consummate your evaluations by the listed due engagement, or sooner, if possible. Other students will be depending on the feedback you lot provide in society to create their final written report. Please refer to the "Course Overview" document for the semester's assignment due dates.
Points: 75
Grading Criteria:
- Evaluations of other students' programs completed in a timely manner. (5)
- Points given to other students' multimedia programs are consequent with the comments provided and with the overall quality of the program. (10)
- Thoughtful evaluations given. Good notes provided, criticism is constructive. (10)
- Evaluation Report includes a summary of strengths and weaknesses of the multimedia program as reported by the three evaluators. (x)
- Evaluation Report encompasses all half dozen criteria - Relevance, Appropriateness, Sufficiency, Instructional Events, and Functionality. (xv)
- Evaluation Report describes revisions that should be made to the multimedia program. (20)
- Link to Evaluation Report added to project web page. (5)
Source: https://www.itma.vt.edu/courses/appliedid/lesson_10.php
0 Response to "Types of Evaluation Small Group One-on-one Expert Review"
Post a Comment